Big Data in Business: Applications of AI
Photo by Mike Kononov on Unsplash
*Before reading this piece, make sure to check out the previous parts of my “Big Data in Business” series:
Part 4: The Lifecycle of an AI Project
To close out this series on big data in business, which has covered the entire transformation of an organization into an AI-driven business, it only makes sense to conclude with the possible business applications following the implementation of an AI solution.
In this final article, we will cover cases from different verticals and industries, such as Sales & Marketing, to give you a sense of the variety of problems AI can tackle.
Sales and Marketing
AI in sales typically involves the use of advanced algorithms and analytical tools that help automate and improve sales operations. The automated operations are usually repetitive tasks and customer data analysis, but machine learning is also used for things like sales forecasting, customer behavior prediction, and to extract valuable insights that can be acted upon.
AI doesn’t just make sales forecasts more accurate, but it also reduces the administrative burden on sales reps and revenue operations with operations like automatically logging sales activities, tracking contract relationships, and sentiment analysis.
When it comes to sales forecasting, AI systems can predict or forecast outcomes by analyzing historical data to inform future results. Some of the common predictions that these AI systems can make include: prospects likely to close, prospects to target next, and new customers. But the quality of the predictions is highly dependent on the quality of the data, which is why it is important for any business to ensure they meet all of the data requirements needed to transform into an AI-driven organization.
>>> To learn more about data and its role in an AI-driven business, check out parts 1 and 2 of this series: “Data Requirements for AI-Driven Businesses” and “Data, Revenue Streams, and Valuations.”
Another use case in sales is lead scoring and prioritization, where AI can analyze large datasets from various sources and indicate which leads should be prioritized.
Regarding lead scoring and prioritization, author and business consultant Victor Antonio once wrote in Harvard Business Review (HBR):
“Often, this decision-making process is based on gut instinct and incomplete information. With AI, the algorithm can compile historical information about a client, along with social media postings and the salesperson’s customer interaction history (e.g., emails sent, voicemails left, text messages sent, etc.) and rank the opportunities or leads in the pipeline according to their chances of closing successfully.”
Besides sales forecasting and lead scoring and prioritization, AI can also recommend sales actions, with the best systems capable of informing teams which actions make the most sense based on the organization's goals and insights from data. Expert recommendations can include everything from how to price a deal to which customers to target next.
Another one of the areas of business drastically impacted by AI is marketing, where companies are adopting solutions to improve operational efficiency while increasing customer experience. Marketers can leverage AI to extract deep insight into their target consumers, with the data then being used to increase conversions and reduce workloads for marketing teams.
One of the specific uses of AI in marketing is to achieve better conversion rate optimization (CRO) and customized website experiences by helping improve the visitor experience through intelligent personalization. Besides the personalization of website experience, intelligent algorithms can also do the same to push notifications, which can be tailored to individual users with behavioral personalization.
Through the use of computer vision, computers and systems can extract meaning from visual inputs like digital images and videos to make recommendations. Marketers can take these recommendations into account when analyzing, for example, millions of photos on social media sites to gain insight into products or services. All of this enables market penetration and brand awareness to be measured in innovative ways.
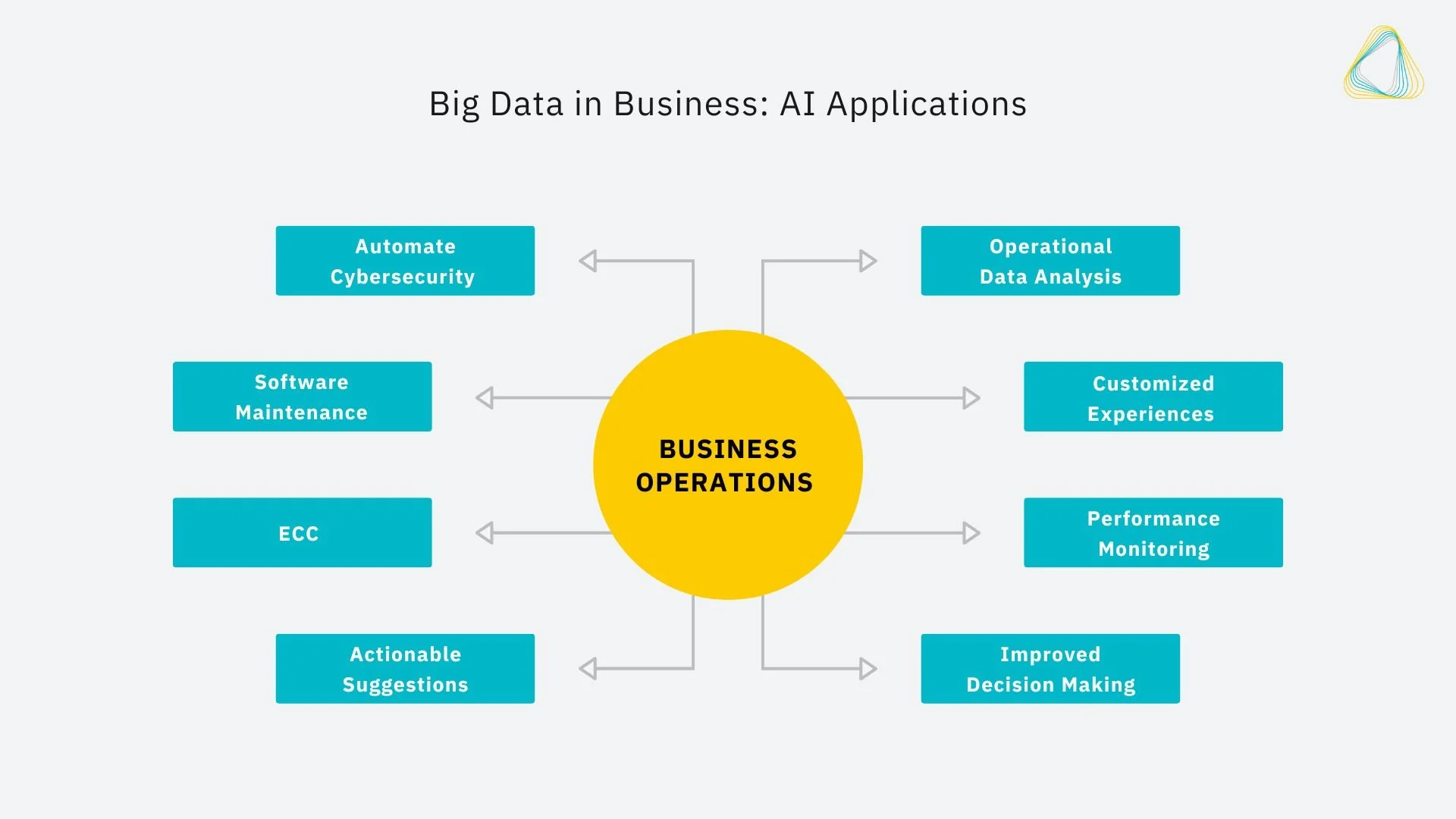
Business Operations
AI is also helping improve business operations across the board. Operations have become complex due to the need for corporate agility, meaning it is difficult for humans to handle. AI automates certain processes to free up staff for higher priority and more valuable tasks.
Businesses save money and resources by improving IT processes through AI. It can automate cybersecurity and software maintenance tasks, or detect potential threats much faster than humans.
Another possible application is enterprise cognitive computing, or ECC, which is a complex combination of AI, machine learning, neural networks, and human interaction. With ECC, the network processes and presents possibilities by studying patterns and making actionable suggestions. In other words, algorithms are used to help humans solve a problem. Rather than being program-based, ECC is problem-based, and it improves the decision-making processes of humans. It is often applied in business processes like supply chain management, buy/sell recommendations, and market expansion planning.
Operational data analysis, which uses company-generated data to improve existing operations, is yet one more area benefited by AI. Humans can only process and synthesize a certain amount of data, but AI and machine learning can enhance operational data analysis by dramatically increasing the speed of data analysis and improving the quality of data synthesis.
>>> Data synthesis is the process of taking raw data and organizing it into a format that is easy to understand and analyze.
Operational data analysis leverages AI to improve human decision-making and analysis rather than replacing humans.
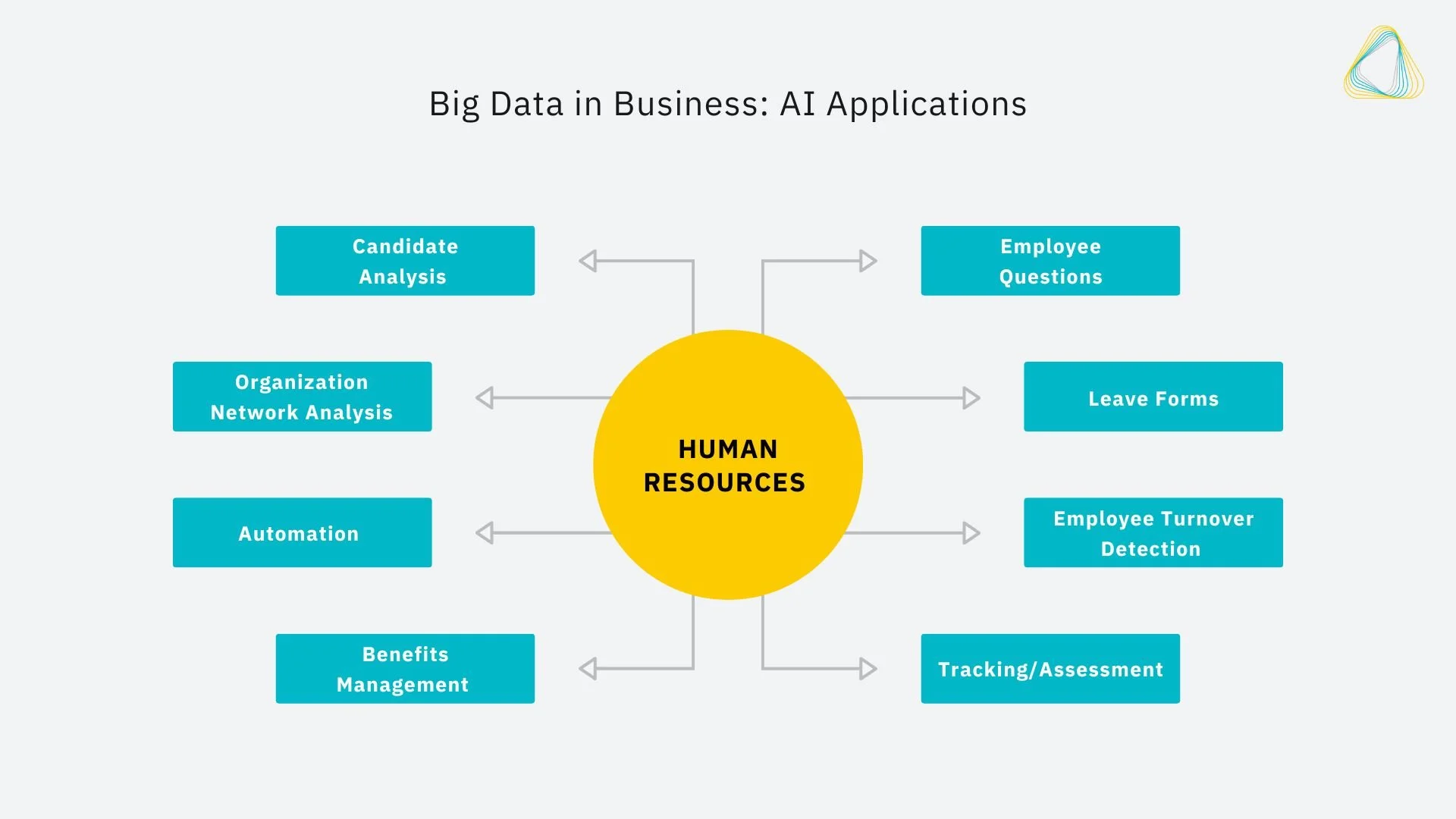
Human Resources
The integration of AI into human resources (HR) is crucial given today’s different business environment due to the COVID-19 pandemic. With remote and hybrid workforces rapidly expanding, as well as virtual recruiting and diversity, AI is introducing new systems while reinforcing existing ones.
Many organizations are now using AI to improve the hiring process, with HR managers using it to analyze a potential candidate’s past experience and interests before matching them with the most appropriate roles. AI is also helping companies with organization network analysis. It can analyze formal and informal relations in the organization, which helps lead to better business strategies that increase the exchange of information.
Perhaps the most obvious application of AI in human resources is to automate time-consuming administrative tasks. Automation is not new to the HR industry, but with the implementation of AI, things look a bit different.
AI can take over all low-value tasks like sifting through applications, where it helps fill important positions quickly by analyzing incoming applications and using algorithms to assess applicants’ experience, knowledge, skills, and more. After bringing on a new hire, AI chatbots help answer typical inquiries regarding benefits, paid time off, and company policies. AI can also craft job descriptions, helping recruiters and HR departments create the best job descriptions while recognizing potential bias in ads.
Automating these types of tasks saves HR professionals time and frees them up to focus on high-value tasks for the organization. And with fewer tasks, they can increase focus on mentoring, motivating and engaging employees, and creating strong workplace relationships.
Customer Support
One of the main goals of any business is to establish a good relationship with its customers, and AI is making this far easier through various tools and techniques. As businesses scale, AI becomes even more important as it is more challenging to keep up with requests.
Customer service teams are deploying chatbots as front-line “customer service agents.” Powered by AI, these bots assist in a variety of ways, including communicating with potential consumers. They can provide assistance 24/7 without the need for a break like humans, and they help consumers get connected to the right people. These bots also help cut wait times and the time needed to answer the same questions over and over. Not only that, but they have access to orders of magnitude greater knowledge bases than a human equivalent, making them much more proficient in supporting customers.
According to IBM, businesses across the globe spend more than $1.3 trillion on 265 billion customer service calls each year. (That’s $1.3 trillion…every year! More than the GDP of most countries.)
AI helps speed up response times, frees up “human agents” for other work, and answers all of the routine questions. Call computerization, which improves conventional interactive voice response systems by combining machine learning and speech recognition, can deliver incredible cost savings over human-powered outsourced call centers. And one of the greatest aspects of synthetic agents is that they often possess multilingual abilities, which is hard to come by with human agents.
The integration of AI in customer service provides many opportunities to increase savings while personalizing and improving an organization’s relationship with customers.
Accounting and Payroll
It’s worth mentioning one more time: One of AI’s greatest powers is automating repetitive and tedious tasks. You can see why AI and accounting are a perfect union.
Accounting involves many repetitive tasks and actions like recording data, reconciling accounts, categorizing transactions, entering data from scanned receipts, evaluating expense reports, and much more, all of which can be automated by AI. Not only does it make these processes more efficient, but they are also far more accurate with less human error.
There are other complex processes that can be semi-automated by AI, such as payroll. Traditional automation is based on cause-and-effect, but AI systems are far more complex, analyzing data, learning from experience, and strategically solving problems. Because AI is expected to play such a big role in the future of payroll, many company executives across industries are integrating advanced AI-supported payroll systems.
Besides these repetitive tasks and payroll, AI is also helping with tasks like transaction coding, invoice fetching, auditing, and real-time compliance monitoring. Some companies must deal with some of these tasks in various languages, which is where AI’s multilingual abilities come in handy once again. Through the use of natural language generation (NLG), it can also analyze data, interpret it, and generate reports efficiently and accurately.
Changing Business Forever
AI has changed business forever, and it will only continue to do so moving forward. Industries are being transformed, with companies of all sizes finding ways to implement AI solutions throughout their organizations.
The implementation of AI is going to become even more diverse with the ability to analyze data across multiple functionalities. It helps identify solutions to highly complex problems, adopting certain characteristics from human intelligence and building on them with algorithms and data.
But we don’t have to look into the future to see what kind of impact AI is having, as noted in this “Big Data in Business” series. Whether it’s Sales and Marketing, Business Operations, Human Resources, Customer Service, Accounting, or some other aspect of a business, AI is extracting insights that were never before possible, automating tedious tasks, and freeing up employees to focus on more high-value tasks in a business. With access to AI being expanded every day, it is now a requirement for any business looking to survive in this data-driven world.
>>> I hope you enjoyed this 5-part series on “Big Data in Business.” Make sure to check out the first four parts to understand the entire process a business undergoes when seeking an AI-driven transformation.
>>> Follow on Twitter, LinkedIn, and Instagram for AI-related content.